- Involves managing all aspects of a customer's relationship with an organization to increase customer loyalty and retention an organization's profitability.
- CRM enables an organization to :
- Provide better customer service
- Make call centers more efficient
- Cross sell products more effectively
- Help sales staff close deals faster
- Simplify marketing and sales processes
- Discover new customers
- Increase customer revenues
RECENCY, FREQUENCY AND MONETARY VALUE
Organizations can find their most valuable customers through "RFM"- Recency, Frequency and Monetary value.
- How recently a customer purchased items (Recency)
- How frequently a customer purchased items (Frequency)
- How much a customer spends on each purchase (Monetary Value)
THE EVOLUTION OF CRM
- CRM reporting technology - help organizations identify their customers across other applications.
- CRM analysis technologies - help organization segment their customers into categories such as best and worst customers.
- CRM predicting technologies - help organizations make predictions regarding customer behavior such as which customers are at risk of leaving.
- Three phases in the evolution of CRM include reporting, analyzing and predicting.
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT'S EXPLOSIVE GROWTH
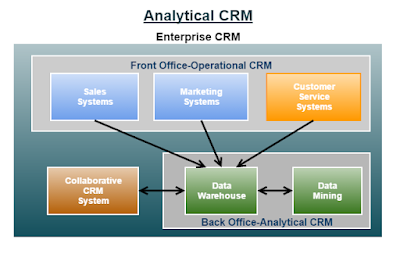
USING ANALYTICAL CRM TO ENHANCE DECISIONS
- Operational CRM - supports traditional transactional processing for day-to-day front-office operations or systems that deal directly with the customers.
- Analytical CRM - supports back-office operations and strategic analysis and includes all systems that do not deal directly with the customers.
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT SUCCESS FACTORS
CRM success factors include :
- Clearly communicate the CRM strategy.
- Define information needs and flows.
- Build an integrated view of the customer.
- Implement in iterations.
- Scalability for organizational growth.







No comments:
Post a Comment